Digital Identity: What's Driving the Market in 2029?

Digital identity systems have become integral to modern society, enabling individuals to access a wide range of services securely and conveniently. As digital interactions increase, the need for robust identity management solutions has grown, leading to the development of various models for handling digital identities.
Juniper Research classifies these into three primary categories: centralised, federated, and decentralised identity systems. Each model offers unique advantages and challenges, reflecting different approaches to security, privacy, and user control. Understanding these forms of digital identity is crucial for navigating the evolving digital landscape and ensuring safe and efficient identity management.
Centralised Identity
Centralised identity systems store digital identity credentials in a single location, used for a specific purpose, with the identity provider handling authentication. A common example is a digital driving license issued by a government. These systems are simple to manage and allow easy access to information, but they pose significant privacy risks due to potential data breaches and often rely on outdated government IT infrastructure.
Federated Identity
Federated identity systems also store identity credentials centrally, but these credentials can be used across multiple systems. This model supports Single Sign-On (SSO), allowing users to access various services with one set of credentials. Examples include India's Aadhaar system. Federated identity systems adhere to principles like user control, minimal data disclosure, and competition among providers. They enhance security and convenience, especially for financial institutions complying with regulations like PSD2 and GDPR. Technologies like JWT and SAML facilitate secure credential sharing across platforms.
Decentralised Identity
In decentralised identity systems, individuals create and manage their credentials, stored in a distributed manner such as on mobile devices. This model replaces traditional logins with cryptographic keys and may use blockchain technology. Users control their information through identity wallets, sharing only necessary details. For example, proving age without disclosing a birth date. Public and private keys in the wallet allow secure interaction with the distributed ledger, ensuring privacy by keeping identity information off the ledger.
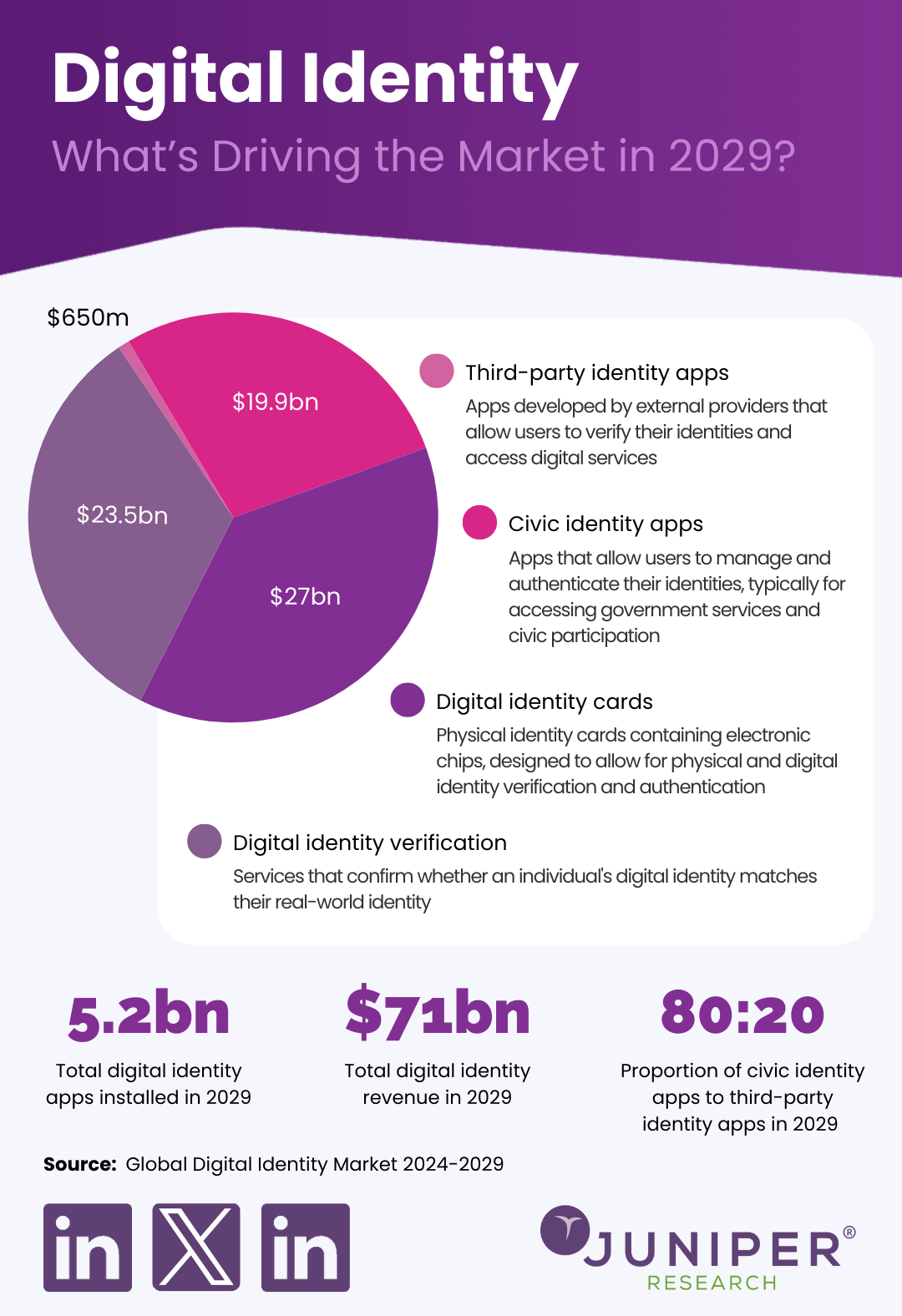
Source: Global Digital Identity Market 2024-2029
Download the Whitepaper: The Anatomy of a Digital ID
Latest research, whitepapers & press releases
-
 ReportMarch 2026Fintech & PaymentsCross-border Payments Market: 2026-2030
ReportMarch 2026Fintech & PaymentsCross-border Payments Market: 2026-2030Our Cross-border Payments research suite provides a comprehensive and in-depth analysis of the evolving cross-border payments landscape; enabling stakeholders such as businesses, financial institutions, payment service providers, card networks, regulators, and technology infrastructure providers to understand future growth, key trends, and the competitive environment.
VIEW -
 ReportFebruary 2026Telecoms & ConnectivityMobile Messaging Market: 2026-2030
ReportFebruary 2026Telecoms & ConnectivityMobile Messaging Market: 2026-2030Juniper Research’s Mobile Messaging research suite provides mobile messaging vendors, mobile network operators, and enterprises with intelligence on how to capitalise on changing market dynamics within the mobile messaging market.
VIEW -
 ReportFebruary 2026Fintech & PaymentsKYC/KYB Systems Market: 2026-2030
ReportFebruary 2026Fintech & PaymentsKYC/KYB Systems Market: 2026-2030Our KYC/KYB Systems research suite provides a detailed and insightful analysis of an evolving market; enabling stakeholders such as financial institutions, eCommerce platforms, regulatory agencies and technology vendors to understand future growth, key trends and the competitive environment.
VIEW -
 ReportFebruary 2026Telecoms & ConnectivityRCS for Business Market: 2026-2030
ReportFebruary 2026Telecoms & ConnectivityRCS for Business Market: 2026-2030Our comprehensive RCS for Business research suite provides an in‑depth evaluation of a market poised for rapid expansion over the next five years. It equips stakeholders with clear insight into the most significant opportunities emerging over the next two years.
VIEW -
 ReportFebruary 2026Fintech & PaymentsMobile Money in Emerging Markets: 2026-2030
ReportFebruary 2026Fintech & PaymentsMobile Money in Emerging Markets: 2026-2030Our Mobile Money in Emerging Markets research report provides detailed evaluation and analysis of the ways in which the mobile financial services space is evolving and developing.
VIEW -
 ReportJanuary 2026IoT & Emerging TechnologyPost-quantum Cryptography Market: 2026-2035
ReportJanuary 2026IoT & Emerging TechnologyPost-quantum Cryptography Market: 2026-2035Juniper Research’s Post-quantum Cryptography (PQC) research suite provides a comprehensive and insightful analysis of this market; enabling stakeholders, including PQC-enabled platform providers, specialists, cybersecurity consultancies, and many others, to understand future growth, key trends, and the competitive environment.
VIEW
-
 WhitepaperMarch 2026Telecoms & Connectivity
WhitepaperMarch 2026Telecoms & ConnectivityMWC 2026: What's Next for Mobile?
Our latest whitepaper distils the most important announcements from MWC Barcelona 2026 and examines what they mean for the telecoms market over the year ahead. From network APIs and 5G monetisation to AI-RAN, direct-to-cell connectivity, and 5G-Advanced, it explains where the biggest opportunities — and challenges — will emerge next.
VIEW -
 WhitepaperMarch 2026Fintech & Payments
WhitepaperMarch 2026Fintech & PaymentsThe Transformation of Cross-border Payment Infrastructure
Our complimentary whitepaper, The Transformation of Cross-border Payment Infrastructure, examines the state of the cross-border payments market; explaining the role of key actors in transforming the cross-border payment experience, as well as the current landscape and recent developments within the cross-border payments industry.
VIEW -
 WhitepaperFebruary 2026Telecoms & Connectivity
WhitepaperFebruary 2026Telecoms & ConnectivityHow Social Media Will Disrupt Mobile Messaging Channels in 2026
Our complimentary whitepaper, How Social Media Will Disrupt Mobile Messaging Channels in 2026, explores the challenges and opportunities for operators and enterprises as social media traffic continues to increase.
VIEW -
 WhitepaperFebruary 2026Telecoms & Connectivity
WhitepaperFebruary 2026Telecoms & ConnectivityProtecting Users from Scam Ads: A Call for Social Media Platform Accountability
In this new whitepaper commissioned by Revolut, Juniper Research examines how scam advertising has become embedded across major social media platforms, quantifies the scale of user exposure and financial harm, and explains why current detection and enforcement measures are failing to keep pace.
VIEW -
 WhitepaperFebruary 2026Fintech & Payments
WhitepaperFebruary 2026Fintech & PaymentsKnow Your Agents (KYA): The Next Frontier in KYC/KYB Systems
Our complimentary whitepaper, Know Your Agents (KYA): The Next Frontier in KYC/KYB Systems, examines the state of the KYC/KYB systems market; considering the impact of regulatory development, emerging risk factors such as identity enabled fraud, and how identity and business verification is evolving beyond traditional customer and merchant onboarding toward agent-level governance.
VIEW -
 WhitepaperFebruary 2026Telecoms & Connectivity
WhitepaperFebruary 2026Telecoms & Connectivity3 Key Strategies for Capitalising on RCS Growth in 2026
Our complimentary whitepaper, 3 Key Strategies for Capitalising on RCS Growth in 2026, explores key trends shaping the RCS for Business market and outlines how mobile operators and platforms can accelerate adoption and maximise revenue over the next 12 months.
VIEW
-
Fintech & Payments
Top Three Global Leaders in Cross-border Payment Infrastructure Revealed
March 2026 -
Telecoms & Connectivity
MVNO Subscriber Revenue to Exceed $50 Billion Globally in 2030
March 2026 -
Fintech & Payments
QUBE Events is excited to bring back the 24th NextGen Payments & RegTech Forum - Switzerland
February 2026 -
Telecoms & Connectivity
OTT Messaging Apps to Exceed 5 Billion Users Globally by 2028; Driving Shift in Enterprise Communication Strategies
February 2026 -
Fintech & Payments
Calling All Fintech & Payment Innovators: Future Digital Awards Now Open for 2026
February 2026 -
Telecoms & Connectivity
Operator RCS for Business Revenue to Reach $3 Billion Globally by 2027, Growing 150% in Two Years
February 2026




















