Fraud-as-a-Service: Inside the Dark Web's Booming Business Model
Fraud-as-a-Service is a cybercrime business model where an individual bad actor provides the necessary tools and services to other bad actors in order to make their fraudulent online activity easier. FaaS schemes are almost indistinguishable from how normal, level businesses - constantly optimising their return on investment through scalable tactics.
Some of the key elements of FaaS include:
- Commodification of Cybercrime: FaaS transforms traditional hacking and fraud methods into services that can be easily purchased or subscribed to; similar to legitimate SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) offerings. FaaS offers a wide range of tactics and personal information that can be used by cybercriminals to commit fraudulent activities.
- Accessibility: FaaS lowers the entry barrier for engaging in cybercrime by providing user-friendly interfaces, tutorials, and customer support. This enables fraudsters of any skill level to successfully commit fraud by purchasing prepackaged scams.
- Diversity of Services: FaaS is not limited to a single tactic, and can facilitate a multitude of different fraudulent attacks. These platforms offer a wide range of services, including but not limited to the tools to commit credit card fraud, identity theft, and DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks. High-end FaaS providers will offer custom-built tools which are tailored towards a client’s specific needs, often focusing on high-value targets.
Typical FaaS Business Structure
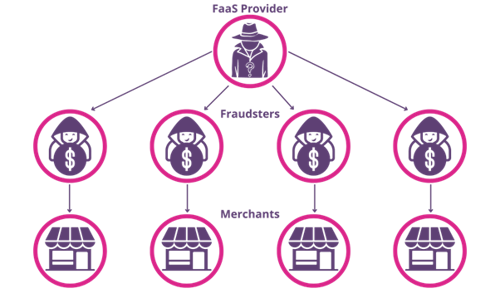
Source: Juniper Research
While it's relatively easy in an online world to attempt a single act of eCommerce fraud anonymously, creating a fraud operation large enough to make it worth the risk requires time, money, and technological expertise. FaaS providers operate beyond the scope of conventional search engines, existing on the dark web which requires specific software for which to gain access. This part of the internet houses illicit forums and marketplaces where FaaS providers can advertise and sell their services to novice fraudsters. This is also accompanied by customer support and user reviews; ensuring customer satisfaction and illustrating how these FaaS schemes operate much like a legitimate business.
What Tools Do FaaS Providers Use?
FaaS providers utilise a vast array of different tools to create their prepackaged schemes and will even rent out the use of these tools to other fraudsters. Some common FaaS tools include:
- App Cloners allow for multiple instances of the same app to be created on the same device and change its source code to enable relevant features. This allows for the bypass of security features that detect multiple account creation.
- Image Injection allows for the inserting of doctored/fraudulent images to spoof verification processes designed to identify new users. This can also be used to submit fraudulent proofs of purchase or delivery confirmations.
- Emulators simulate different devices and environments; helping to mimic legitimate device activity at scale, avoiding detection.
- Application Tampering Techniques enable individuals to change certain information that is collected from them on an application. For instance, things such as location spoofing can be used to manipulate the geographical location of a device to evade services that rely on location data.
- Botnets leverage up to thousands of infected computers to conduct DDoS attacks or leverage clicks on ads that are placed on fraudulent websites for example.
Tools such as the aforementioned are used to enable fraud attacks such as ATO (Account Takeover) fraud, refund fraud, online payment fraud, and synthetic identity fraud. They are either used by the FaaS provider to create fraud packages to sell, or are rented out to individual fraudsters on a subscription basis.
Furthermore, FaaS providers may have access to stolen payment card information, healthcare records, or social media accounts. They can use this data to create fake users, which are then sold or rented to subscribers, or they simply sell the raw data to fraudsters to create their own fake accounts. FaaS has democratised online financial crime for fraudsters that do not possess the necessary technical knowledge and has made committing fraud more accessible than ever before.
How Much of a Threat Does FaaS Pose to Businesses?
The FaaS model is akin to the SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) model, meaning that fraudulent information and tools are easily accessible to dark web users. By lowering this barrier for entry, businesses are at an increased risk of fraud attacks. This, in addition to the employment of artificial intelligence and machine learning amongst fraudulent methods, has resulted in bad actors being able to focus on the rapid execution of attacks.
The financial damage caused by FaaS-supported attacks can be devastating, and further potential revenue can be lost through consumer trust in the business being spoilt. In order to defend against FaaS tactics effectively, proactive fraud prevention strategies are essential. Things such as velocity checks, which analyse the rate at which users are completing transactions, and geolocation, which monitors the location from which a user is attempting their transaction, can help to accurately determine whether a user’s behaviour is illegitimate or not. App tampering and device emulation are also metrics that merchants can analyse in order to halt attacks with greater accuracy.
Therefore, it is possible for merchants to defend against the threats that FaaS poses, but it is imperative that the fraud prevention strategies they employ continually evolve in order to keep pace with the emerging threats that FaaS enables.
Latest research, whitepapers & press releases
-
 ReportJanuary 2026IoT & Emerging Technology
ReportJanuary 2026IoT & Emerging TechnologyPost-quantum Cryptography Market: 2026-2035
Juniper Research’s Post-quantum Cryptography (PQC) research suite provides a comprehensive and insightful analysis of this market; enabling stakeholders, including PQC-enabled platform providers, specialists, cybersecurity consultancies, and many others, to understand future growth, key trends, and the competitive environment.
VIEW -
 ReportJanuary 2026Telecoms & Connectivity
ReportJanuary 2026Telecoms & ConnectivityMVNO in a Box Market: 2026-2030
Juniper Research’s MVNO in a Box research suite provides Mobile Virtual Network Enablers, Mobile Virtual Network Aggregators, and other players with detailed analysis and strategic recommendations for monetising demand for MVNO in a Box services.
VIEW -
 ReportDecember 2025
ReportDecember 2025AI Agents for Customer Experience Platforms Market: 2025-2030
Our comprehensive AI Agents for Customer Experience Platforms research suite comprises detailed assessment of a market that is set to disrupt mobile communications. It provides stakeholders with insight into the key opportunities within the AI agents for customer experience platforms market over the next two years.
VIEW -
 ReportDecember 2025Fintech & Payments
ReportDecember 2025Fintech & PaymentseCommerce Fraud Prevention Market: 2025-2030
Our eCommerce Fraud Prevention research suite provides a detailed and insightful analysis of this evolving market; enabling stakeholders from financial institutions, law enforcement agencies, regulatory bodies and technology vendors to understand future growth, key trends, and the competitive environment.
VIEW -
 ReportNovember 2025Telecoms & Connectivity
ReportNovember 2025Telecoms & ConnectivityeSIMs & iSIMs Market: 2025-2030
Juniper Research’s eSIMs and iSIMs research suite offers insightful analysis of a market set to experience significant growth in the next five years. The research suite provides mobile network operators (MNOs), original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and eSIM management and platforms vendors with intelligence on how to capitalise on the market growth, and guidance on how eSIM-only devices and sensors, SGP.42, in-factory provisioning, and iSIMs will change the competitive landscape.
VIEW -
 ReportNovember 2025Fintech & Payments
ReportNovember 2025Fintech & PaymentsModern Card Issuing Platforms Market: 2025-2030
Our Modern Card Issuing Platforms Market research suite provides a detailed and insightful analysis of this evolving market; enabling stakeholders from banks, financial institutions, fintech companies, and technology vendors to understand future growth, key trends, and the competitive environment.
VIEW
-
 WhitepaperJanuary 2026IoT & Emerging Technology
WhitepaperJanuary 2026IoT & Emerging TechnologyPreparing for Q-Day: Post-quantum Security Shift
Our complimentary whitepaper, Preparing for Q-Day: Post-quantum Security Shift, assesses the factors which are increasing interest in adopting PQC, and challenges to PQC adoption. Additionally, it includes a forecast summary of the global spend on PQC by 2035.
VIEW -
 WhitepaperJanuary 2026Telecoms & Connectivity
WhitepaperJanuary 2026Telecoms & ConnectivityHow Fintechs and Retail Companies Are Changing Mobile Services
Our complimentary whitepaper, How Fintechs and Retail Companies Are Changing Mobile Services, explores the key enterprises entering the MVNO market and launching mobile services via MVNO in a Box partners. It also provides forecasts for total MVNO revenue from mobile subscribers in 2030.
VIEW -
 WhitepaperJanuary 2026IoT & Emerging Technology
WhitepaperJanuary 2026IoT & Emerging TechnologyTop 10 Emerging Tech Trends 2026
See which emerging technologies will shape enterprise strategy and investment in 2026; from post-quantum cryptography to neuromorphic computing and next-generation infrastructure.
VIEW -
 WhitepaperDecember 2025Telecoms & Connectivity
WhitepaperDecember 2025Telecoms & ConnectivityHuman + AI: Drivers of Customer Experience AI Agents in 2026
Our complimentary whitepaper, Human + AI: Drivers of Customer Experience AI Agents in 2026, examines the key drivers of the AI agents for customer experience platforms market in 2025.
VIEW -
 WhitepaperDecember 2025Fintech & Payments
WhitepaperDecember 2025Fintech & PaymentsBeyond Chargebacks: The True Cost of Fraud for Digital Commerce
Our complimentary whitepaper, Beyond Chargebacks: The True Cost of Fraud for Digital Commerce, examines the state of the eCommerce fraud prevention market; considering the impact of evolving digital fraud strategies, including key trends such as identity theft, account takeovers, chargebacks, policy abuse and friendly fraud.
VIEW -
 WhitepaperNovember 2025Telecoms & Connectivity
WhitepaperNovember 2025Telecoms & ConnectivityeSIM-only Devices: The Impact on Operators, Consumers, and IoT
Our complimentary whitepaper, eSIM-only Devices: The Impact on Operators, Consumers, and IoT, explores the challenges and opportunities for the three segments, with a particular focus on eSIM-only smartphones and SGP.42.
VIEW
-
Fintech & Payments
Civic Identity Apps, Tokenisation, & AI to Revolutionise Fraud & Security Globally in 2026
January 2026 -
Telecoms & Connectivity
eSIM Connections to Reach 1.5bn Globally in 2026, But Platforms Must Adapt to Fuel Growing IoT Demand
January 2026 -
Fintech & Payments
Modern Card Issuing Platforms to Issue 1.6 Billion Payment Cards in 2030, as Banks Shift Focus From UX to Cost Efficiency
January 2026 -
IoT & Emerging Technology
Post-quantum Cryptography Market to Exceed $13 Billion by 2035 as Q-Day Awareness Accelerates
January 2026 -
Fintech & Payments
Digital Wallets: QR Codes to Constitute Half of All Wallet Transactions Globally Over Next Five Years
January 2026 -
Telecoms & Connectivity
MVNO in a Box Platforms to Drive MVNO Market to 438 Million Subscribers Globally by 2030
January 2026


















